A Double Materiality assessment provides a thorough understanding of the business’s most significant ESG impacts, risks, and opportunities.
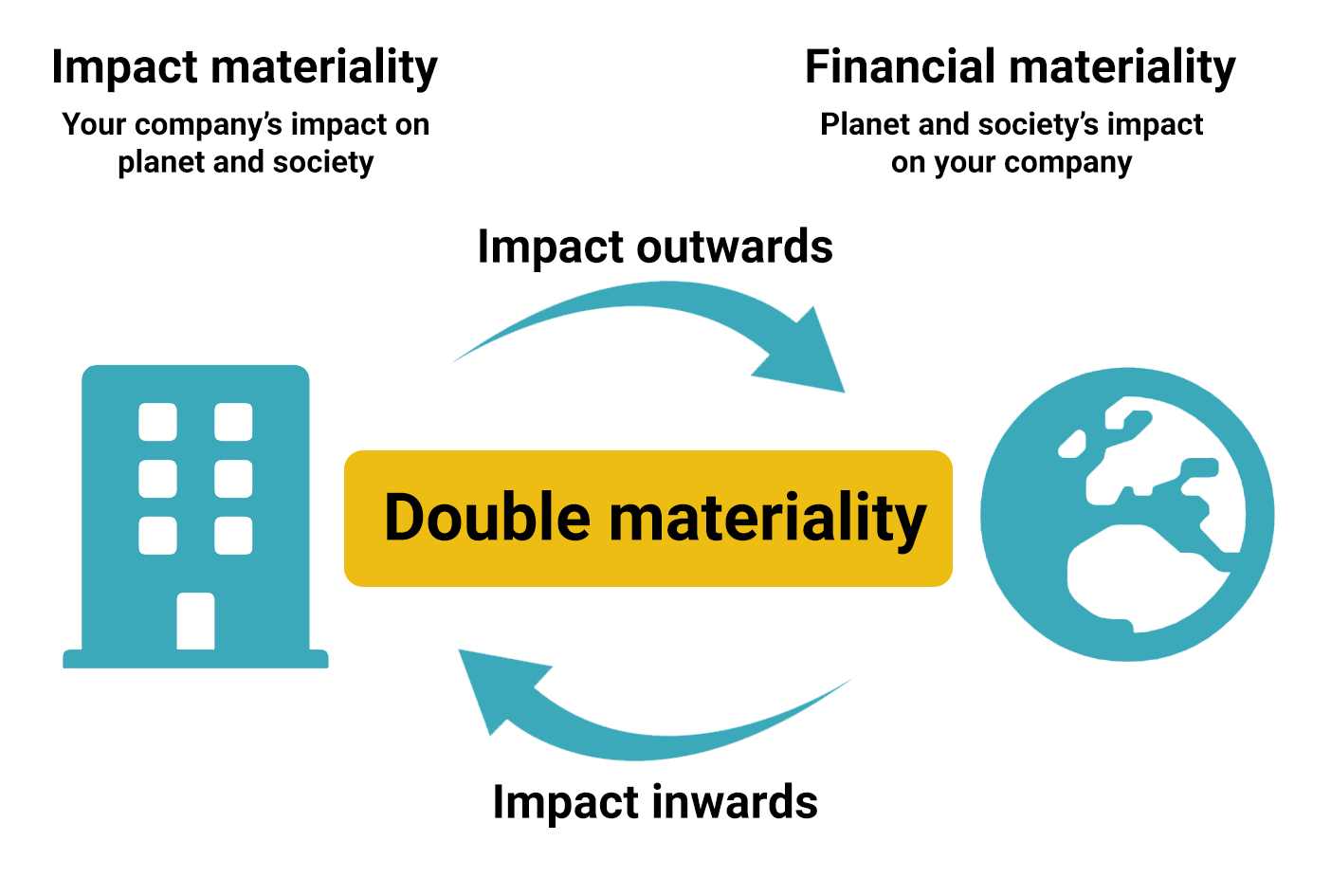
A Double Materiality assessment is an in-depth process and is stakeholder informed, drawing on industry norms, expert opinion, and international frameworks and standards. With the Corporate Sustainability Reporting Directive (CSRD), conducting a double materiality assessment has become compulsory for affected companies, as further elaborated in the European Sustainability Reporting Standards (ESRS). A double materiality assessment examines both the positive and negative impacts of the business on society and the environment, as well as the ESG-related risks and opportunities. This gives a company a ‘dual-lens’ through which to understand both its impact on the world and how ESG factors could affect its financial and/or operational performance. It allows a company to amplify its contributions to the UN Sustainable Development Goals and to future-proof its business. Engaging stakeholders in the materiality assessment process also has the added benefit of deepening your understanding of stakeholder expectations and strengthening relationships with key stakeholder groups.
Double Materiality Assessment Process
Phase 1: Organisational Context Mapping
This first phase generates an understanding of the ESG landscape in which the organisation operates, involving value chain mapping, stakeholder mapping, analysis of industry practice, and review of regulations and relevant frameworks.
Phase 2: Identifying Impacts, Risks and Opportunities
The second phase is crucial to identify the sustainability matters relevant to the organisation and link these to the corresponding impacts, risks, and opportunities. Internal and external stakeholder groups are engaged, for example, through in-depth interviews, focus groups, and surveys, to better understand their expectations of the company and their assessment of sustainability matters.
Phase 3: Assessing and Determining Material Impacts, Risks and Opportunities
In the third phase, all insights are brought together and the identified impacts, risks, and opportunities are assessed in working sessions with internal experts, applying the agreed-upon methodology. A high-level validation and prioritisation with senior management is the final step towards a list of material impacts, risks, and opportunities. For showcasing the results, a form of visualisation such as a materiality matrix is chosen.
Phase 4: Materiality Assessment Report
The final step encompasses writing a summary report, which includes descriptions of the reporting process, stakeholder engagement, methodology, and guidance on the next steps. The report will support the company in preparing for any regulatory reporting, including the assurance process, and provide vital insights for furthering its ESG strategy.
Contact Us
If you’d like to discuss this in person, please contact us on info@sustainable-advantage.com.

